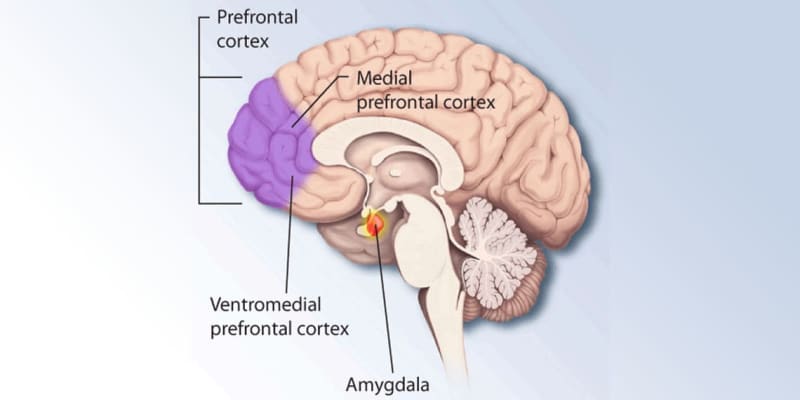
A neuroimaging study involving 28-year-olds in Belgium discovered that individuals with mothers who experienced higher levels of anxiety during pregnancy exhibited weaker functional connectivity between the medial prefrontal cortex and the left inferior frontal gyrus regions of the brain. This diminished connectivity could lead to challenges in emotional regulation, decision-making, and stress management. The findings were published in the journal Brain Imaging and Behavior.
During the previous decade, many studies utilizing neuroimaging techniques reported links between maternal psychological distress or mental health issues during pregnancy and the characteristics of the brain of their children. Scientists propose that this might mean that mental health issues of mothers affect the development of the fetal brain, creating changes that last into adulthood.
Of these mental health issues, anxiety and depression are the most common. A study in the UK estimated that treating anxiety and depression of mothers at the time of pregnancy costs the society around 8500 GBP per woman giving birth. Anxiety is a mental health condition characterized by persistent feelings of worry, fear, or tension, often in response to perceived threats or stressors.
Study author Elise Turk and her colleagues wanted to investigate the links between anxiety of mothers during pregnancy and the functional characteristics of specific brain areas of their children, after they have become adults. They had a unique opportunity to study individuals participating in a longitudinal study that started 28 years before their investigation.
The study involved 52 participants, all 28 years old, whose mothers were part of a longitudinal study that began in 1986. During the initial study, these women were between 18 to 30 weeks pregnant, had no pregnancy-related complications or medical risks, and were not using any drugs or medications harmful to the fetus. All participants were Dutch-speaking and completed the State Trait Anxiety Inventory (STAI) to assess anxiety levels. Based on these assessments, researchers categorized them into “high anxiety” and “low-to-medium anxiety” groups. These assessments were repeated multiple times: during pregnancy, when their child was 1, 10, and 28 weeks old, and then again at ages 8/9, 14/15, 17, and 20 years.
In 2014 and 2015, the offspring, now 28 years old, underwent functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) scans of their brains at a university hospital.
Results showed that individuals whose mothers were in the high anxiety group tended to have weaker functional connectivity between the medial prefrontal cortex and left prefrontal cortex with some other brain regions in the left hemisphere. Additional analyses using other methods of inquiry confirmed these findings and also revealed an additional association of weaker connectivity between left lateral prefrontal cortex with left somatosensory motor gyrus.
The medial prefrontal cortex region of the brain plays a pivotal role in decision-making, social behavior, and self-reflection. It acts as a central component in processing information about oneself and others, including empathy, moral judgments, and risk assessment. It is also involved in emotional regulation, helping to modulate responses to stress and fear.
On the other hand, the left prefrontal cortex is closely associated with experiences of positive emotions, motivation, and the regulation of the body’s response to stress. It has a critical function in language processing, working memory, and executive functions, such as planning and decision-making. If the connectivity between the medial prefrontal cortex and the left prefrontal cortex is weakened, it may lead to difficulties in emotional regulation, decision-making, and coping with stress, potentially exacerbating symptoms of anxiety and depression.
The study sheds light on the links between mental health conditions of expectant mothers and the development of infant brains. However, it also has limitations that need to be taken into account. Notably, the number of study participants was very small and they were purposively selected for the study. Results might not be the same on a larger group of participants, more representative of the general population. Additionally, the design of the study does not allow any cause-and-effect inferences to be drawn from the results.
The paper, “Maternal anxiety during pregnancy is associated with weaker prefrontal functional connectivity in adult offspring“, was authored by Elise Turk, Marion I. van den Heuvel, Charlotte Sleurs, Thibo Billiet, Anne Uyttebroeck, Stefan Sunaert, Maarten Mennes, and Bea R.H. Van den Bergh.
